« Translations:IA et cybersécurité/3/en » : différence entre les versions
Page créée avec « == The security of intelligent systems and their uses in cybersecurity, state of knowledge and skills == vignette|300x300px|left Artificial Intelligence systems are becoming more and more widespread in modern information technology, and have made many advances in recent years. With a view to preparing the next generations of applications and defense systems against cyber threats, the Cyber Campus, through the Artif... » |
Aucun résumé des modifications |
||
| Ligne 1 : | Ligne 1 : | ||
== The security of intelligent systems and their uses in cybersecurity, state of knowledge and skills == | == The security of intelligent systems and their uses in cybersecurity, state of knowledge and skills == | ||
[[ | [[Fichier:GT IA & Cyber - Focus du Groupe de Travail.png|vignette|300x300px|gauche]] | ||
Artificial Intelligence systems are becoming more and more widespread in modern information technology, and have made many advances in recent years. With a view to preparing the next generations of applications and defense systems against cyber threats, the Cyber Campus, through the Artificial Intelligence and Cybersecurity Working Group, is highlighting the main uses of AI to benefit cybersecurity, the limits identified as well as the risks and main measures recommended for the security of these systems. | Artificial Intelligence systems are becoming more and more widespread in modern information technology, and have made many advances in recent years. With a view to preparing the next generations of applications and defense systems against cyber threats, the Cyber Campus, through the Artificial Intelligence and Cybersecurity Working Group, is highlighting the main uses of AI to benefit cybersecurity, the limits identified as well as the risks and main measures recommended for the security of these systems. | ||
Dernière version du 5 décembre 2023 à 15:27
The security of intelligent systems and their uses in cybersecurity, state of knowledge and skills
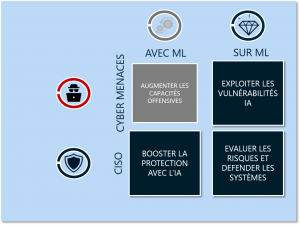
Artificial Intelligence systems are becoming more and more widespread in modern information technology, and have made many advances in recent years. With a view to preparing the next generations of applications and defense systems against cyber threats, the Cyber Campus, through the Artificial Intelligence and Cybersecurity Working Group, is highlighting the main uses of AI to benefit cybersecurity, the limits identified as well as the risks and main measures recommended for the security of these systems.
Which players are involved in Artificial Intelligence projects?
Artificial Intelligence projects involve a wide range of players in order to make the most of the data and respond to the use case identified in advance. Identifying key resources is a major challenge for any cybersecurity expert at the start of a project, and a succinct description of roles and responsibilities helps to quickly identify the stakeholders. The various phases of an AI project, including the development, production launch and monitoring of an AI application, involve many players, some of whom are data science specialists, others not. The diagram below shows the four main families of players identified:
- "Business" profiles, in charge of the use case and its validation in relation to the company's objectives;
- Data science specialists, in charge of implementing Artificial Intelligence techniques to meet the needs identified by the "business";
- IT profiles, in charge of developing and putting into production the use cases designed by the data science specialists;
- Risk profiles, in charge of monitoring and ensuring compliance with internal policies and external regulations.
